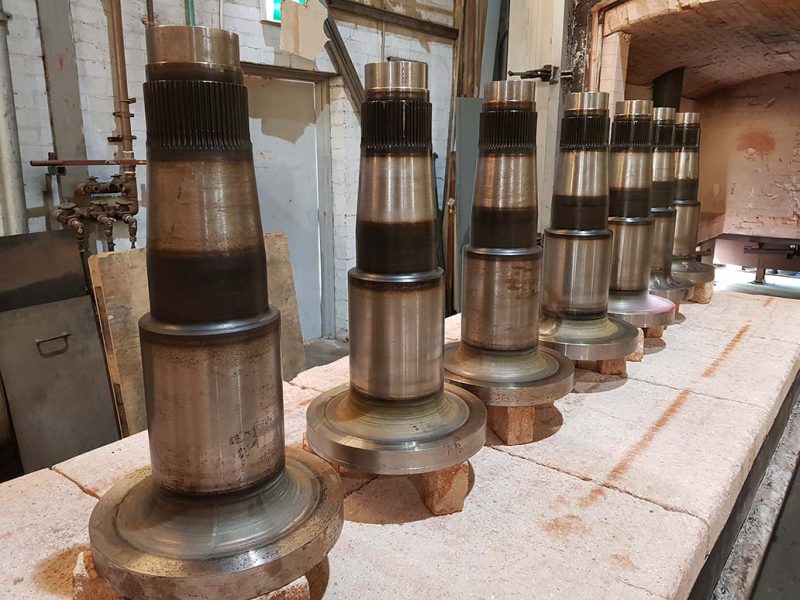
The nitriding process with two furnaces enhances metal durability and hardness. Alpha Detroit Heat Treatment offers this process Australia-wide.
The nitriding process is a heat treatment technique used to improve the surface hardness and wear resistance of metals. By using two furnaces in the process, Alpha Detroit Heat Treatment optimises the procedure for greater precision and consistency.
Serving clients across Australia and New Zealand, we specialise in advanced nitriding solutions for industries requiring durable, high-performance metal components.
What is Nitriding?
Nitriding is a thermochemical treatment process where nitrogen atoms are diffused into the surface of a metal, typically steel, at temperatures between 500°C and 550°C. This results in the formation of hard nitrides on the surface, which significantly enhances the material’s wear resistance, fatigue strength, and surface hardness. Unlike other heat treatment processes, nitriding is performed at lower temperatures, which means it doesn’t require quenching and thus avoids thermal distortion.
The Two-Furnace Nitriding Process
The nitriding process with two furnaces involves the use of two distinct furnaces in a sequential manner, typically a pre-heating furnace and a nitriding furnace. This two-step approach helps to ensure better control over the process, particularly in terms of temperature, atmosphere, and consistency of results.
The first furnace in the two-furnace nitriding process is the preheating furnace. This furnace is used to gradually raise the temperature of the workpieces to a level that is suitable for nitriding but not yet high enough to start the nitrogen diffusion. The main purpose of the preheating furnace is to:
• Avoid Thermal Shock: Gradually heating the material helps to avoid thermal shock, which can cause cracking or distortion in the components.
• Ensure Uniform Heating: It ensures that the workpieces are uniformly heated before they enter the nitriding furnace, which is critical for achieving consistent nitriding results.
The preheating furnace typically operates at temperatures between 300°C and 400°C, depending on the material being treated. Once the parts are pre-heated, they are transferred to the nitriding furnace.
The nitriding furnace is where the actual nitriding process takes place. This furnace operates at higher temperatures, usually between 500°C and 550°C, in a controlled nitrogen-rich atmosphere. In the nitriding furnace, nitrogen gas is introduced into the chamber, and the metal surface absorbs nitrogen atoms. The nitrogen diffuses into the surface layer, forming hard nitrides, such as iron nitrides, which enhance the material’s hardness and wear resistance.
Two-Furnace Nitriding by Experts
The two-furnace system allows for better control of both the pre-heating and nitriding stages, resulting in more consistent and reliable results. Additionally, the gradual heating process in the pre-heating furnace helps to reduce the risk of distortion, a common issue in single-furnace nitriding.
The use of two furnaces also ensures that the workpieces reach the nitriding stage at the optimal temperature, leading to more efficient nitrogen diffusion and improved surface properties. Lastly, the two-furnace system can handle multiple components at once, improving the overall throughput of the nitriding process.
The nitriding process with two furnaces offers better control over the process, reduced distortion, and improved material properties. By using a pre-heating furnace followed by a nitriding furnace, heat treatment experts like Alpha Detroit Heat Treatment can achieve more consistent and reliable results, making this method ideal for high-performance components used in industries like automotive, aerospace, and tooling.
Optimized by: Netwizard SEO